What Are The Indicators Of Heel Spur

Overview
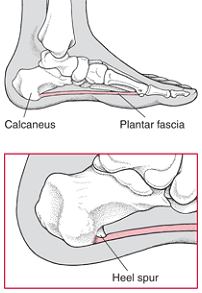
Heel spurs, pointed, bony outgrowths of the heel, are caused by localized soft tissue inflammation and can be located at the back of the heel or under the heel, beneath the sole of the foot. Plantar fascitis is associated with inflammation caused by heel spurs on the soles of the feet. Both conditions are treated with ice application and anti-inflammatory medications. Orthotics may also provide some relief.
Causes
Heel Spurs develop when the plantar fascia is excessively and repetitively pulled away from the heel bone. In many cases, a heel spur can develop along with plantar fasciitis, but can also occur by itself. Heel spurs often develop in middle-aged patients, but can also occur in younger people as well. Athletes are especially prone to heel spur due to the regular stress on their heels.
Symptoms
Heel spurs can be quite painful, but can just as likely occur with no symptoms at all. Plantar fasciitis is a contributing condition to heel spurs. The cause of the pain is not the heel spur itself but the soft-tissue injury associated with it. The feeling has been described as a knife or pin sticking into the bottom of your feet when you first stand up after sitting or laying down for a long period of time - a pain that later turns into a dull ache.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made using a few different technologies. X-rays are often used first to ensure there is no fracture or tumor in the region. Then ultrasound is used to check the fascia itself to make sure there is no tear and check the level of scar tissue and damage. Neurosensory testing, a non-painful nerve test, can be used to make sure there is not a local nerve problem if the pain is thought to be nerve related. It is important to remember that one can have a very large heel spur and no plantar fasciitis issues or pain at all, or one can have a great deal of pain and virtually no spur at all.
Non Surgical Treatment
In case of heel spurs rest is most important. Active sports, running, long walks etc should be avoided to start with. If you?re in a job that requires a lot of standing, take a few days off work. Rest (or reduced activity) is essential to allow the inflammation from becoming aggrevated. Furthermore, you can use ice packs (placed on the heel for 5-10 minutes) to ?cool down? the inflamed area. You may take anti-inflammatory medication or apply a topical inflammatory (i.e. a cream) to help reduce inflammation. In addition, there are some simple exercises that should be done daily to help relieve heel spur pain.
Surgical Treatment
Though conservative treatments for heel spurs work most of the time, there are some cases where we need to take your treatment to the next level. Luckily, with today?s technologies, you can still often avoid surgery. Some of the advanced technologies to treat a Heel Spur are Platelet Rich Plasma Therapy. Platelet Rich Plasma Therapy (also known as PRP) is one of several regenerative medicine techniques that University Foot and Ankle Institute has helped bring to foot and ankle care. This amazing in-office procedure allows the growth factors in the blood to be used to actually begin the healing process again long after your body has given up on healing the area. Heel Pain Shockwave Therapy. Shockwave therapy is a non-invasive procedure done in the office that allows for new blood to get to the region of fascia damage and help with healing. Results have been excellent with more than 70 percent of patients getting relief with only one treatment. Topaz for Heal Spurs and pain. Another minimally invasive technology technique is called Coblation Surgery using a Topaz probe. This minimally invasive procedure involves controlled heating of multiple tiny needles that are inserted through the skin and into the plantar fascia. This process, like PRP and Shockwave therapy, irritates the fascia enough to turn a chronic problem back into an acute problem, greatly increasing the chances of healing. Heel Spur Surgery. Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy is one surgical procedure that we consider to release the tight fascia. University Foot and Ankle Institute has perfected an endoscopic (camera guided) approach for fascia release to allow rapid healing and limited downtime with minimal pain.